- Java Code Formatter Lib
- Download Dr Java For Mac
- Java Games Code For Mac
- Java Code For Mac
- Java Code For Machine Learning Algorithms
Hello World in Java on Mac OS X Step 1: Open TextEdit Application. To write your code, you will use a text editor application included on all Mac OS X. Step 2: Configure TextEdit for Java Programming. First you must configure the text editor for java code. On the menu bar. Step 3: Create a.
- Class
Class Mac
- Jul 29, 2019 Today, we bring you a line up of text editors for Mac users that are sure to meet all your coding requirements while offering reliability and security. Visual Studio Code. Visual Studio Code is an open-source source code editor created and maintained by Microsoft. It is designed with beauty, ease-of-use, and speed in mind, coupled with.
- Java+You, Download Today! Java Download » What is Java? » Uninstall About Java.
- Drag Visual Studio Code.app to the Applications folder, making it available in the macOS Launchpad. Add VS Code to your Dock by right-clicking on the icon to bring up the context menu and choosing Options, Keep in Dock. Launching from the command line. You can also run VS Code from the terminal by typing 'code' after adding it to the path.
- Compiling and running a Java application on Mac OSX, or any major operating system, is very easy. Apple includes a fully-functional Java runtime and development environment out-of-the-box with OSX, so all you have to do is write a Java program and use the built-in tools to compile and run it.
- javax.crypto.Mac
- All Implemented Interfaces:
- Cloneable
This class provides the functionality of a 'Message Authentication Code' (MAC) algorithm.A MAC provides a way to check the integrity of information transmitted over or stored in an unreliable medium, based on a secret key. Typically, message authentication codes are used between two parties that share a secret key in order to validate information transmitted between these parties.
A MAC mechanism that is based on cryptographic hash functions is referred to as HMAC. HMAC can be used with any cryptographic hash function, e.g., SHA256 or SHA384, in combination with a secret shared key. HMAC is specified in RFC 2104.
Every implementation of the Java platform is required to support the following standard
Macalgorithms:- HmacMD5
- HmacSHA1
- HmacSHA256
- Since:
- 1.4
Constructor Summary
Constructors Modifier Constructor and Description protectedMac(MacSpi macSpi, Provider provider, String algorithm)
Method Summary
Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description Objectclone()Returns a clone if the provider implementation is cloneable.byte[]doFinal()byte[]doFinal(byte[] input)Processes the given array of bytes and finishes the MAC operation.voiddoFinal(byte[] output, int outOffset)StringgetAlgorithm()Returns the algorithm name of thisMacobject.static MacgetInstance(String algorithm)Returns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.static MacgetInstance(String algorithm, Provider provider)Returns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.static MacgetInstance(String algorithm, String provider)Returns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.intgetMacLength()ProvidergetProvider()Returns the provider of thisMacobject.voidinit(Key key)voidinit(Key key, AlgorithmParameterSpec params)Initializes thisMacobject with the given key and algorithm parameters.voidreset()voidupdate(byte input)Processes the given byte.voidupdate(byte[] input)voidupdate(byte[] input, int offset, int len)Processes the firstlenbytes ininput, starting atoffsetinclusive.voidupdate(ByteBuffer input)Processesinput.remaining()bytes in the ByteBufferinput, starting atinput.position().Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object
equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait
Constructor Detail
Mac
- Parameters:
macSpi- the delegateprovider- the provideralgorithm- the algorithm
Method Detail
getAlgorithm
Returns the algorithm name of thisMacobject.This is the same name that was specified in one of the
getInstancecalls that created thisMacobject.- Returns:
- the algorithm name of this
Macobject.
getInstance
Returns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.This method traverses the list of registered security Providers, starting with the most preferred Provider. A new Mac object encapsulating the MacSpi implementation from the first Provider that supports the specified algorithm is returned.
Note that the list of registered providers may be retrieved via the
Security.getProviders()method.- Parameters:
algorithm- the standard name of the requested MAC algorithm. See the Mac section in the Java Cryptography Architecture Standard Algorithm Name Documentation for information about standard algorithm names.- Returns:
- the new
Macobject. - Throws:
NoSuchAlgorithmException- if no Provider supports a MacSpi implementation for the specified algorithm.- See Also:
Provider
getInstance
Returns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.A new Mac object encapsulating the MacSpi implementation from the specified provider is returned. The specified provider must be registered in the security provider list.
Note that the list of registered providers may be retrieved via the
Security.getProviders()method.- Parameters:
algorithm- the standard name of the requested MAC algorithm. See the Mac section in the Java Cryptography Architecture Standard Algorithm Name Documentation for information about standard algorithm names.provider- the name of the provider.- Returns:
- the new
Macobject. - Throws:
NoSuchAlgorithmException- if a MacSpi implementation for the specified algorithm is not available from the specified provider.NoSuchProviderException- if the specified provider is not registered in the security provider list.IllegalArgumentException- if theprovideris null or empty.- See Also:
Provider
getInstance
Returns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.A new Mac object encapsulating the MacSpi implementation from the specified Provider object is returned. Note that the specified Provider object does not have to be registered in the provider list.
- Parameters:
algorithm- the standard name of the requested MAC algorithm. See the Mac section in the Java Cryptography Architecture Standard Algorithm Name Documentation for information about standard algorithm names.provider- the provider.- Returns:
- the new
Macobject. - Throws:
NoSuchAlgorithmException- if a MacSpi implementation for the specified algorithm is not available from the specified Provider object.IllegalArgumentException- if theprovideris null.- See Also:
Provider
getProvider
- Returns:
- the provider of this
Macobject.
getMacLength
Returns the length of the MAC in bytes.- Returns:
- the MAC length in bytes.
init
- Parameters:
key- the key.- Throws:
InvalidKeyException- if the given key is inappropriate for initializing this MAC.
init
Initializes thisMacobject with the given key and algorithm parameters.- Parameters:
key- the key.params- the algorithm parameters.- Throws:
InvalidKeyException- if the given key is inappropriate for initializing this MAC.InvalidAlgorithmParameterException- if the given algorithm parameters are inappropriate for this MAC.
update
- Parameters:
input- the input byte to be processed.- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
update
Processes the given array of bytes.- Parameters:
input- the array of bytes to be processed.- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
update
Processes the firstlenbytes ininput, starting atoffsetinclusive.- Parameters:
input- the input buffer.offset- the offset ininputwhere the input starts.len- the number of bytes to process.- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
update
Processesinput.remaining()bytes in the ByteBufferinput, starting atinput.position(). Upon return, the buffer's position will be equal to its limit; its limit will not have changed.- Parameters:
input- the ByteBuffer- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.- Since:
- 1.5
doFinal
Finishes the MAC operation.A call to this method resets this
Macobject to the state it was in when previously initialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec). That is, the object is reset and available to generate another MAC from the same key, if desired, via new calls toupdateanddoFinal. (In order to reuse thisMacobject with a different key, it must be reinitialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec).- Returns:
- the MAC result.
- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
doFinal
Finishes the MAC operation.A call to this method resets this
Macobject to the state it was in when previously initialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec). That is, the object is reset and available to generate another MAC from the same key, if desired, via new calls toupdateanddoFinal. (In order to reuse thisMacobject with a different key, it must be reinitialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec).The MAC result is stored in
output, starting atoutOffsetinclusive.- Parameters:
output- the buffer where the MAC result is storedoutOffset- the offset inoutputwhere the MAC is stored- Throws:
ShortBufferException- if the given output buffer is too small to hold the resultIllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
doFinal
Processes the given array of bytes and finishes the MAC operation.A call to this method resets this
Macobject to the state it was in when previously initialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec). That is, the object is reset and available to generate another MAC from the same key, if desired, via new calls toupdateanddoFinal. (In order to reuse thisMacobject with a different key, it must be reinitialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec).- Parameters:
input- data in bytes- Returns:
- the MAC result.
- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
reset
Resets thisMacobject.A call to this method resets this
Macobject to the state it was in when previously initialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec). That is, the object is reset and available to generate another MAC from the same key, if desired, via new calls toupdateanddoFinal. (In order to reuse thisMacobject with a different key, it must be reinitialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec).
clone
Returns a clone if the provider implementation is cloneable.- Overrides:
clonein classObject- Returns:
- a clone if the provider implementation is cloneable.
- Throws:
CloneNotSupportedException- if this is called on a delegate that does not supportCloneable.- See Also:
Cloneable
- Class
- Summary:
- Nested |
- Field |
- Constr |
- Detail:
- Field |
- Constr |
Submit a bug or feature
For further API reference and developer documentation, see Java SE Documentation. That documentation contains more detailed, developer-targeted descriptions, with conceptual overviews, definitions of terms, workarounds, and working code examples.
Copyright © 1993, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Use is subject to license terms. Also see the documentation redistribution policy.
Scripting on this page tracks web page traffic, but does not change the content in any way.
In a better world, no one would have to use Java anymore. Sadly there are still university programs where people are expected to use Java. Rather than cast people into the world of Eclipse, here are instructions on how to get Xcode building Java. These instructions are current as of Xcode 4.6.2. You will need to download a JDK from somewhere.
This is a basic environment meant only for writing simple school programs. It has no debugger. Replace <MyProject> with whatever you want to name your project. Your main project file, main project class, and Xcode project must use this name. Welcome to Java.
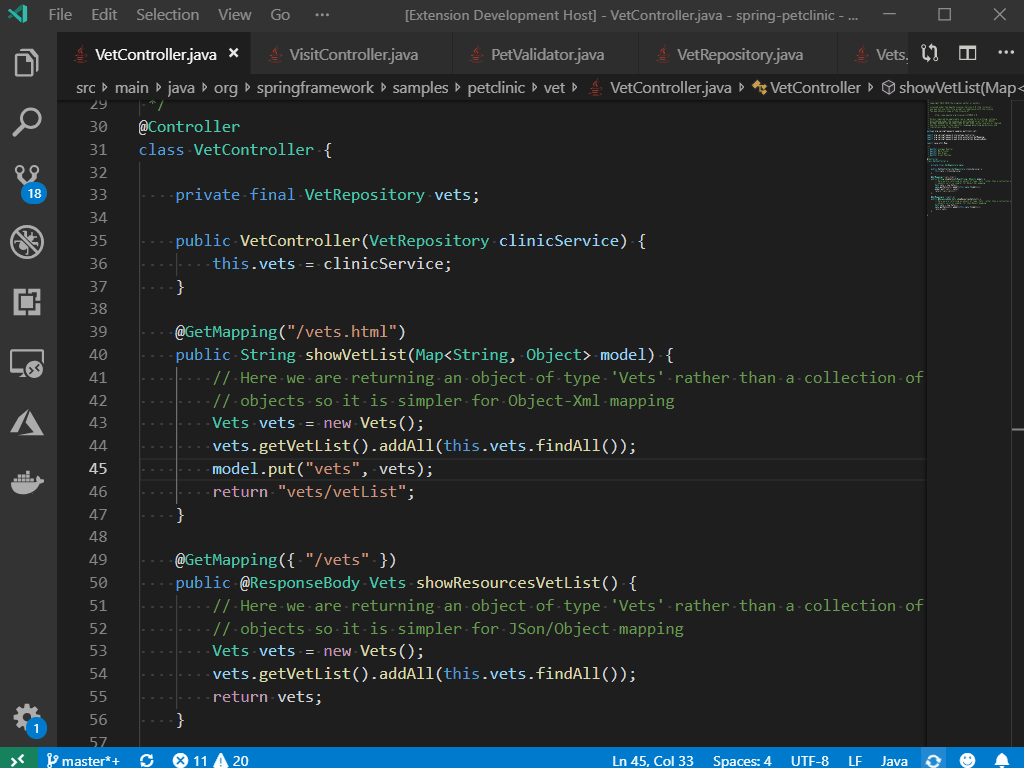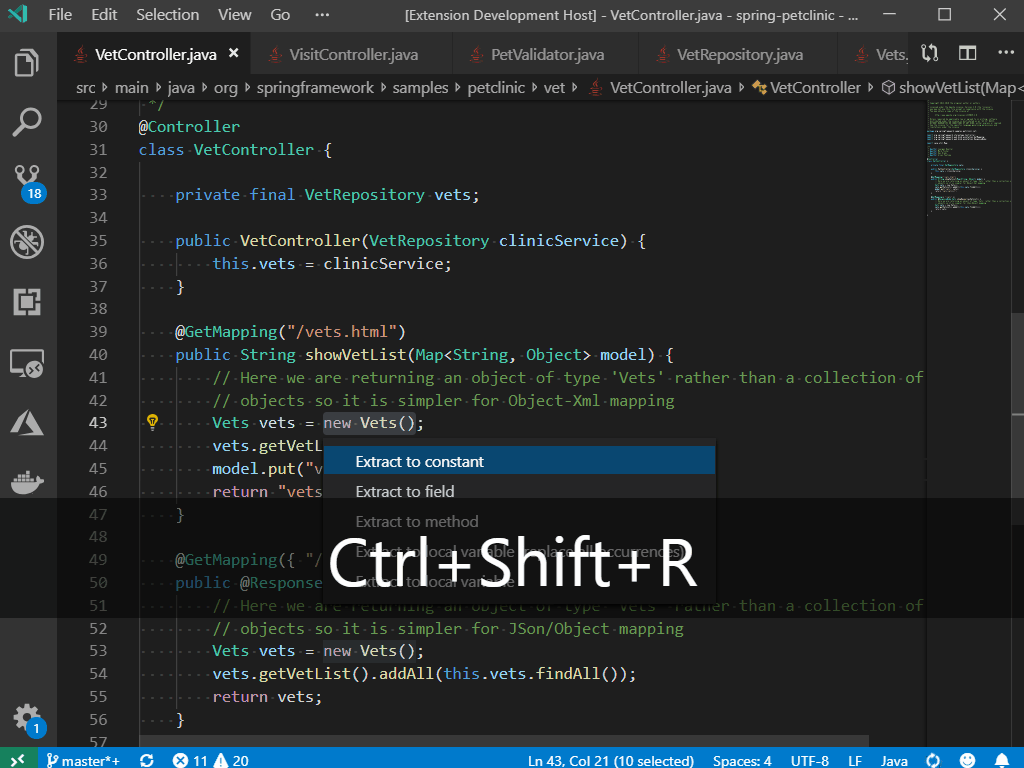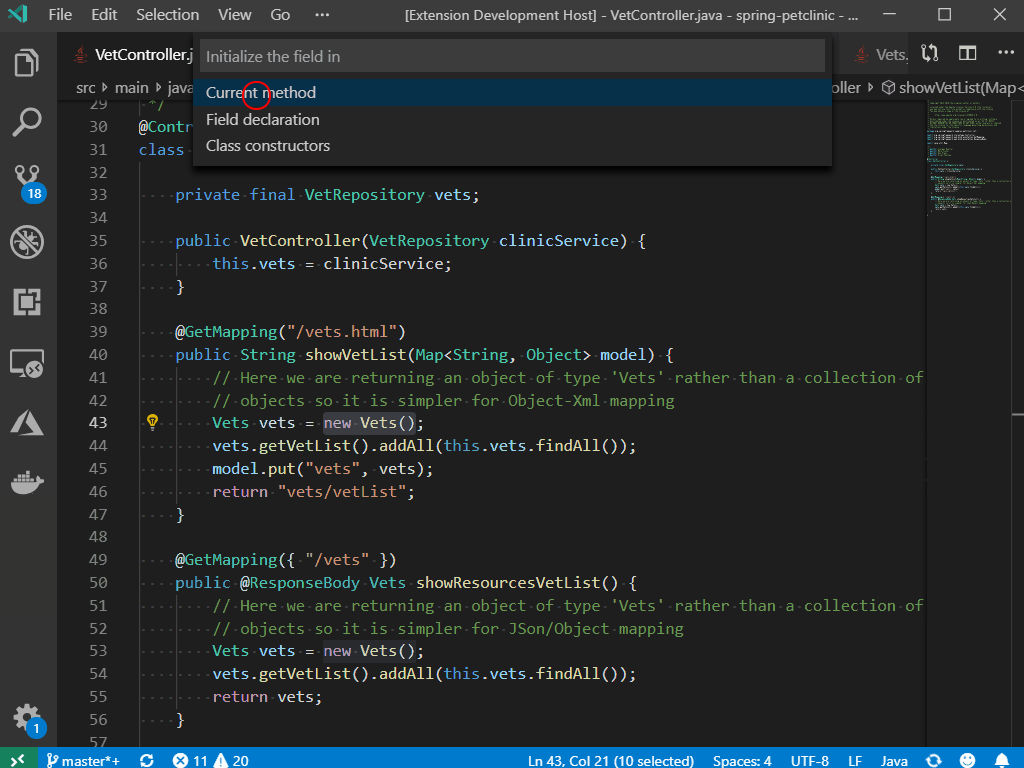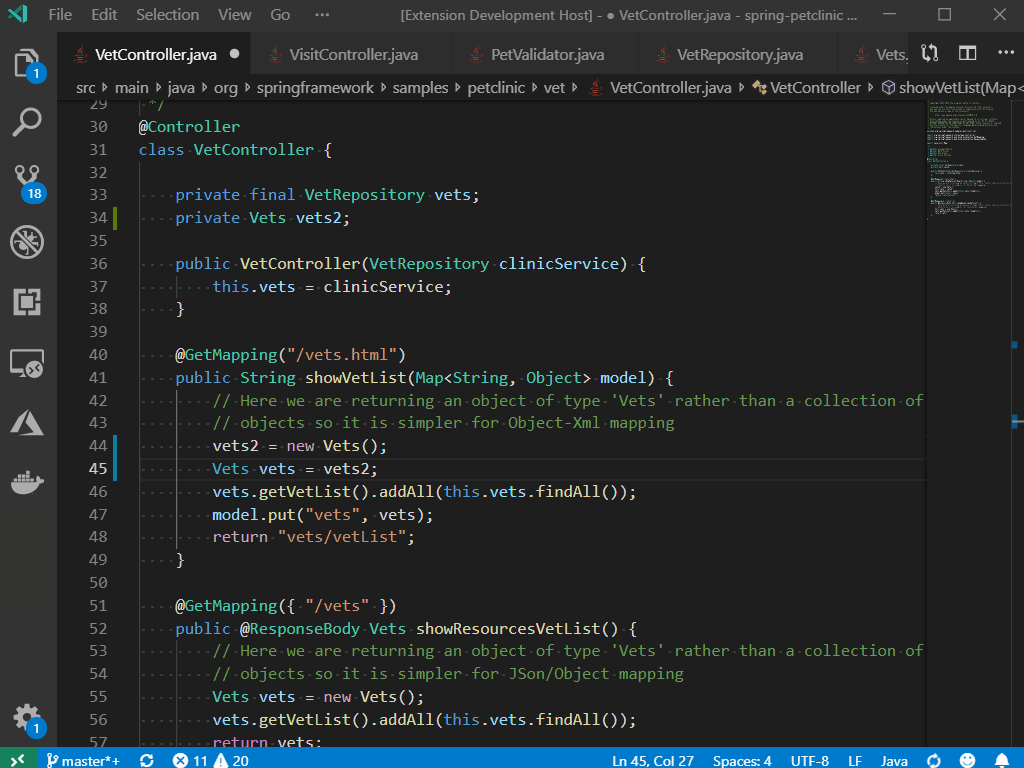
1) In Xcode, File > New > New Project > Other > External Build System
2) Give it a meaningful name <MyProject> and save it somewhere. Note the name. You'll need that later.
3) File > New > New File > Other > Empty
4) Give it a Java-friendly name. In my example, use <MyProject>.java
5) Copy the contents below into the file and save.
6) File > New > New File > Other > Empty
7) Save as Makefile.
8) Copy the contents below into the file and save.
9) The 'Run' (>) button should at least compile your Java now.
Now it gets tricky. You don't have to do the next part. You could just open a Terminal to your project directory and run java <MyProject> if you want. I strongly suggest that. You can also just type 'make' and use Xcode purely as a text editor.
9) Project > Scheme > Edit Scheme > Debug > Info tab
10) Executable > Other > type ^⌘g > type /usr/bin > choose java
11) Change Debugger to None
12) Arguments tab
13) For Arguments Passed on Launch, add $(TARGETNAME)
14) For Environment Variables, add CLASSPATH with a value of $(PROJECT_DIR)

15) For Expand Variables based on, use <MyProject>
16) Click the 'Run' (>) button.
PS: I have no idea how to run the Java debugger in Xcode. But then, I have no idea how to run the Java debugger at all.
Here are some starter file contents:
HelloWorld.java:
publicclass HelloWorld
{
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println('Hello, World!');
}
}
Makefile:
# A simple makefile for a Hello World Java program
# Define a makefile variable for the java compiler
JCC = javac

# Define a makefile variable for compilation flags
# The -g flag compiles with debugging information
JFLAGS = -g
# typing 'make' will invoke the first target entry in the makefile
# (the default one in this case)
default: $(subst .java,.class,$(wildcard *.java))
# this target entry builds the Average class
# the Average.class file is dependent on the Average.java file
# and the rule associated with this entry gives the command to create it
#
%.class : %.java
$(JCC) $(JFLAGS) $<
Java Code Formatter Lib
# To start over from scratch, type 'make clean'.
# Removes all .class files, so that the next make rebuilds them
#
clean:
$(RM) *.class

Download Dr Java For Mac
Java Games Code For Mac
NOTE: Those indentations are true tab characters. Ugh!
Java Code For Mac
Java Code For Machine Learning Algorithms
Good luck on your class. Hopefully you can progress onto more complicated projects and eventually use a real language like Objective-C.
