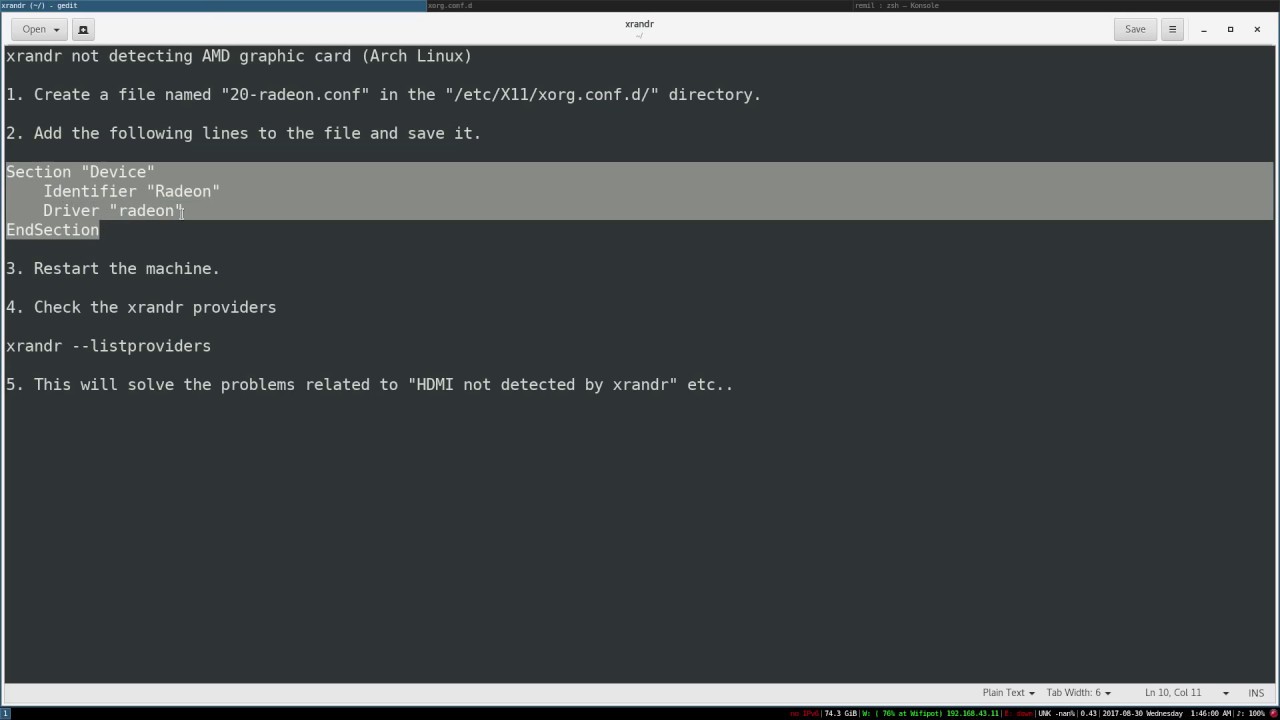
Xorg Macports

FreeBSD supports security extensions based on the POSIX®.1e draft. These security mechanisms include file system Access Control Lists (Section 13.9, “Access Control Lists”) and Mandatory Access Control (MAC). MAC allows access control modules to be loaded in order to implement security policies. Some modules provide protections for a narrow subset of the system, hardening a particular service. Others provide comprehensive labeled security across all subjects and objects. The mandatory part of the definition indicates that enforcement of controls is performed by administrators and the operating system. This is in contrast to the default security mechanism of Discretionary Access Control (DAC) where enforcement is left to the discretion of users.
This chapter focuses on the MAC framework and the set of pluggable security policy modules FreeBSD provides for enabling various security mechanisms.

Xorg-x11-xauth architectures: aarch64, armv7hl, i586, i686, x8664. Xorg-x11-xauth linux packages: rpm ©2009-2020 - Packages Search for Linux and Unix. On FreeBSD, Xorg can be installed as a package or port. The binary package can be installed quickly but with fewer options for customization: # pkg install xorg. To build and install from the Ports Collection: # cd /usr/ports/x11/xorg # make install clean. Either of these installations results in the complete Xorg system being installed. The Xquartz project is an open-source effort to develop a version of the X.org X Window System that runs on Mac OS X. Together with supporting libraries and applications, it. XMind is the most professional and popular mind mapping tool. Millions of people use XMind to clarify thinking, manage complex information, run brainstorming and get work organized. Xming, free and safe download. Xming latest version: Run This Display Server For Free On Windows. The Xming program is better known as a.

After reading this chapter, you will know:
The terminology associated with the MAC framework.
The capabilities of MAC security policy modules as well as the difference between a labeled and non-labeled policy.
The considerations to take into account before configuring a system to use the MAC framework.
Which MAC security policy modules are included in FreeBSD and how to configure them.
How to implement a more secure environment using the MAC framework.
How to test the MAC configuration to ensure the framework has been properly implemented.
Before reading this chapter, you should:
Understand UNIX® and FreeBSD basics (Chapter 3, FreeBSD Basics).
Have some familiarity with security and how it pertains to FreeBSD (Chapter 13, Security).
Warning:
Xorg-macros Debian
Improper MAC configuration may cause loss of system access, aggravation of users, or inability to access the features provided by Xorg. More importantly, MAC should not be relied upon to completely secure a system. The MAC framework only augments an existing security policy. Without sound security practices and regular security checks, the system will never be completely secure.
The examples contained within this chapter are for demonstration purposes and the example settings should not be implemented on a production system. Implementing any security policy takes a good deal of understanding, proper design, and thorough testing.
Xorg For Mac
While this chapter covers a broad range of security issues relating to the MAC framework, the development of new MAC security policy modules will not be covered. A number of security policy modules included with the MAC framework have specific characteristics which are provided for both testing and new module development. Refer to mac_test(4), mac_stub(4) and mac_none(4) for more information on these security policy modules and the various mechanisms they provide.
